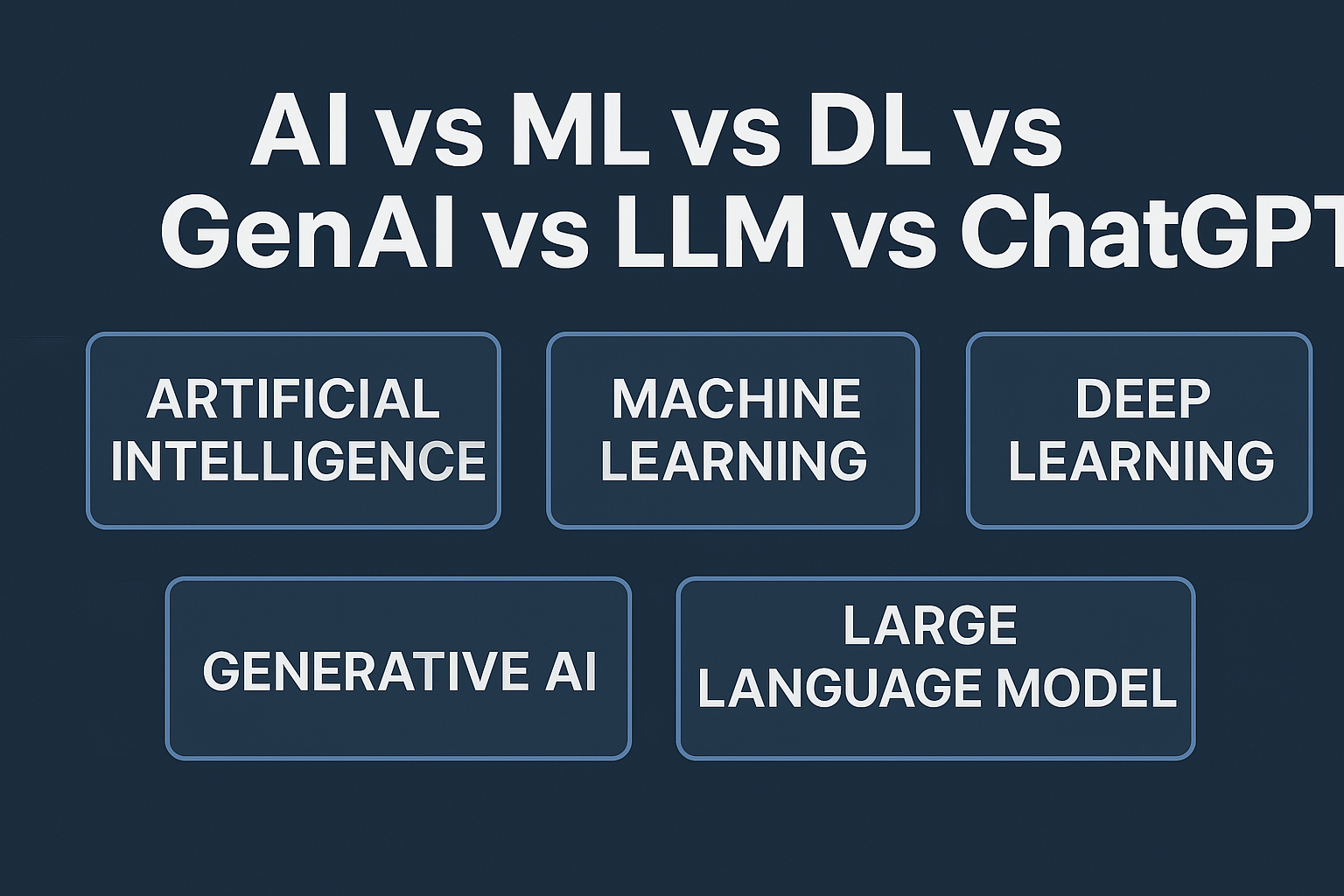
The AI revolution is being powered by an ecosystem that is growing at an astonishing pace—and at the heart of it lies the Large Language Model (LLM). These models, trained on vast corpora of text, have evolved from academic experiments into the backbone of cutting-edge products, from intelligent chatbots to AI research assistants and beyond.
But deploying an LLM in the real world is not as simple as plugging in a model and flipping a switch. Behind the scenes is a rich and dynamic LLM ecosystem made up of tools, platforms, workflows, and best practices—all working together to create scalable, intelligent applications.
In this post, we’ll explore the key components of the LLM ecosystem, unpack the tools that power it, and share how developers and organizations are building next-generation AI solutions.
What Are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models are neural networks trained to understand and generate human-like text. Models like GPT-4, Claude, LLaMA, and PaLM are capable of tasks such as answering questions, summarizing content, writing code, and holding conversations—thanks to their vast knowledge and deep contextual understanding.
The true magic, however, lies not just in the models, but in the ecosystem that supports them.
The Key Components of the LLM Ecosystem
1. Model Training
This is where the foundation is laid. LLMs are trained on large datasets using powerful infrastructure like GPUs or TPUs.
- Frameworks: PyTorch, TensorFlow, JAX.
- Tools: Hugging Face Transformers, DeepSpeed, Megatron-LM.
- Compute Providers: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, CoreWeave.
Model training is typically handled by large labs or companies due to the high computational cost, but open models like Mistral, LLaMA, and Falcon are increasingly enabling the community to contribute and experiment.
2. Fine-Tuning and Adaptation
After pretraining, models can be fine-tuned on specific datasets to specialize in tasks (e.g., customer support, legal analysis).
- Tools:
- Hugging Face
TrainerAPI - LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation)
- PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning)
- QLoRA (for fine-tuning large models with lower compute)
- Hugging Face
Fine-tuning allows organizations to customize base models for their unique domain needs without retraining from scratch.
3. Inference and Deployment
Once trained, LLMs must be served efficiently. This step deals with running the models in real time or batch mode.
- Frameworks:
- vLLM: Optimized for LLM inference.
- Triton, ONNX Runtime, TensorRT: For model optimization and deployment.
- Platforms:
- Hugging Face Inference Endpoints
- Replicate
- Modal
- RunPod
- OpenAI API (as a managed service)
Latency, cost, and scalability are crucial at this stage, especially when serving millions of users.
4. Vector Databases and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
LLMs alone don’t “know” everything. RAG is used to augment LLMs with fresh or domain-specific knowledge via search.
- Vector Databases:
- Pinecone
- Weaviate
- FAISS
- Chroma
- Tools: LangChain, LlamaIndex
These tools let developers store embeddings (numerical representations of text) and retrieve them in real time to provide contextually accurate answers.
5. Orchestration and Agent Frameworks
Combining prompts, tools, APIs, and memory, orchestration frameworks enable intelligent multi-step reasoning.
- LangChain: A popular framework for chaining together prompts, tools, and agents.
- Semantic Kernel: Microsoft’s take on AI-first app development.
- Autogen: Orchestrates multiple LLM agents to collaborate on tasks.
- OpenAI Functions / Tools API: Lets GPT call APIs and plug into external systems.
6. Prompt Engineering and Evaluation
Crafting the right prompt can be the difference between an insightful response and gibberish.
- Prompt Engineering Techniques:
- Few-shot / Zero-shot prompting
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT)
- ReAct (Reason + Act)
- Evaluation Tools:
- TruLens
- PromptLayer
- LangSmith
- HumanEval (for code models)
LLM performance is hard to measure with traditional metrics, so specialized eval systems are key for quality assurance.
Real-World Applications: How It All Comes Together
Let’s look at how different parts of the ecosystem are combined in practice.
AI Tutor
- Base Model: GPT-4
- Fine-Tuning: Domain-specific knowledge in education
- RAG: Retrieve from a curated knowledge base of textbooks
- Orchestration: LangChain agent handling questions, quizzes, summaries
- Deployment: vLLM on GPU servers
- Evaluation: Student feedback loop and automated scoring metrics
Legal Document Analyzer
- Base Model: LLaMA 2
- Fine-Tuning: On legal contracts and terminology
- Vector DB: FAISS storing legal precedents
- Prompting: CoT prompting for contract interpretation
- UI Layer: Integrated with Slack via OpenAI Tools API
The Road Ahead
The LLM ecosystem is expanding rapidly, with trends like:
- Open models and decentralization (e.g., Mistral, Mixtral)
- On-device inference with quantized models
- Multi-agent systems that collaborate autonomously
- AutoML for LLMs, enabling no-code fine-tuning and evaluation
Final Thoughts
Building with LLMs today means more than just calling an API. It’s about orchestrating a dynamic ecosystem of tools, frameworks, and services to deliver intelligent, personalized, and efficient experiences at scale.
As the ecosystem continues to evolve, so too will the sophistication of the applications we can build—ushering in a new era of AI-powered systems that are more autonomous, more adaptive, and more human-like than ever before.
Want more deep dives like this?
Subscribe to the blog or follow us on social to stay up-to-date on the latest in AI engineering and tooling.